UPSC IAS Mains Exam 2020 - HISTORY (Paper-1)
Time Allowed : 3.00 Hrs Maximum Marks : 250
SECTION 'A'
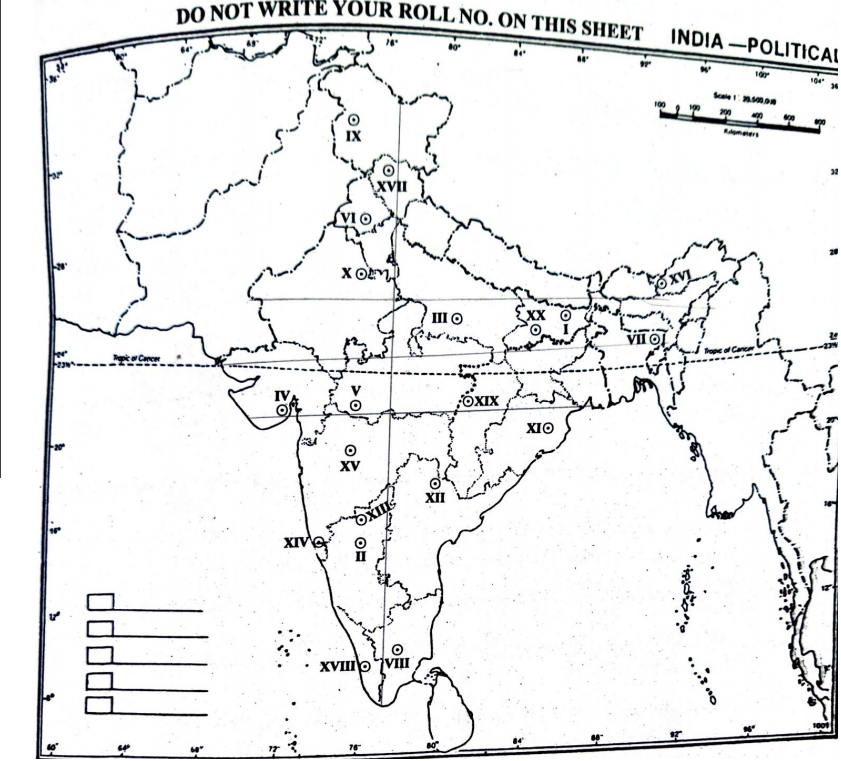
Q1. Identify the following places marked on the map supplied to you and write a short note of about 30 words on each of them in your Question-cum-Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of the places marked on the map are given below seriatim.
- (i) Paleolithic site is no
- (ii) Paleolithic Factory site
- (iii) Neolithic site
- (iv) Early and Mature Harappan site
- (v) Chalcolithic site
- (vi) Site of Coin and Seal Moulds
- (vii) Ancient Administration Centre
- (viii) Ancient Political Headquarter
- (ix) Ancient Temple site
- (x) Pre and Proto Historic sites
- (xi) Ancient Capital City
- (xii) Place of Shaiva Temple
- (xiii) World Heritage Centre of Temple complex
- (xiv) An Inscriptional site
- (xv) Place of Jain Temple
- (xvi) Largest Buddhist Monastery
- (xvii) Ancient Temple Complex
- (xviii) Place of oldest Mosque
- (xix) Temple Complex dedicated to Shiva
- (xx) Ancient Education Centre
Q2.(a) Puranas were the innovative genre of literature to popularise and revive Vedic religion. Elaborate with examples.
2.(b) Discuss the factors that played an important role in the process of urbanisation : after the Later-Vedic period. .
2.(c) Throw light on the nature of religion and classification of gods mentioned in the Rigveda.
Q3.(a) Evaluate the significant political features of the Post Mauryan Northern India. What are the main sources of it?
3.(b) A number of scholars considered Alexander as 'The Great', although long term impacts of Alexander's invasion on India need to be re-evaluated. Comment. 15.
3.(c) Discuss the salient features of cultural traditions of South India as reflected in Sangam Literature.
Q4.(a) Sanskrit literature of classical Gupta Age set standards for the early medieval India. Evaluate the statement with representative examples.
4.(b) Trace and identify the changing pattern of Tantrism in Ancient India with examples.
4.(c) Describe the evolution and development of regional temple architecture of South India with special reference to Pallavas.
SECTION 'B'
Q5.Answer the following questions in about 150 words each :
5.(a) Critically evaluate the Muslim Nobility during the period of Tughlaq dynasty.
5.(b) Describe in detail about the foreign travellers' accounts which gave information of Vijayanagar kingdom.
5.(c) How did international trade support urbanisation in North India during the 13-14th century CE.
5.(d) Evaluate the aim and impact of the translation of Sanskrit scriptures into Persian language during Mughal period.
5.(e) Examine the sources of the history of Chhatrapati Shivaji with special reference to Shivabharat and Sabhasad Bakhar.
Q6.(a) Assess the causes of the defeat of Northern Indian States against the Turkish invasion.
6.(b) Amuktamalyada dwells much upon the relationship of (fort, Brahmanas) and dispersed tribal groups. Comment.
6.(c) Elaborate upon the agrarian reforms of Alauddin Khilji.
Q7.(a) Describe village polity and economy of medieval Deccan.
7.(b) Some new crafts production were introduced by the Turks. Comment.
7.(c) The mission of Kabir was to preach a religion of love which would unite all castes and creeds. Explain.
Q8.(a) Evaluate the contribution of Sher Shah towards trade and commerce, administration and agricultural reforms.
8.(b) Make an estimate of the development of paintings under Mughal reference to colours, technique, themes and influences on them. paintings under Mughal rulers with special
8.(c) Critically evaluate history of the Eighteenth century India with reference to culture and economy.
UPSC IAS Mains Exam 2020 - HISTORY (Paper-2)
Time Allowed : 3.00 Hrs Maximum Marks : 250
SECTION 'A'
Q1. Critically examine the following statements in about 150 words each :
(a) "Maharaja Ranjit Singh died in 1839. His death was the signal for an outburst of anarchy all over the Punjab."
(b) “In the initial stages, when Indian nationalism was immature, just sprouting, it found expression in many liberal religio-reform movements."
(c) “In the early twentieth century, there came into existence a number of women's organisations, which operated more actively in the public arena and focused more directly on women's political and legal rights."
(d) “The Trade Union Movement in India not only supported the call for national struggle at critical junctures, but also impacted its course and character in several ways."
(e) “Based on his discussion with Indian leaders, as well as his own perception, Lord Mountbatten soon came to the conclusion that partition was the only practicable and feasible solution."
Q2.(a) It was Dupleix who had first showed the way of intervening of the Indian rulers and thereby acquiring political control over vast territories — a technique which was later perfec India Company." Elaborate.
(b) For long, the Revolt of 1857. has been mistaken to be a mere mutiny of me Indian sepoys in the Bengal army. However, its causes need to be searched for not only in the dissatisfaction of the army but in a long arawn process of fundamental Social and economic change that upset the peasant communities./Discuss.
(c) Do you feel that the Santhal Hool (rebellion) 1855-56, was the most effective tribal movement in pre-1857 India ?
Q3.(a) In its political behaviour the Indian National Congress in its early career was never a radical organisation, besides the founders of the Congress involved A.O. Hume in their project. Do these facts verify that the Congress was founded as a 'Safety valve' ? Explain.
(b). Do you agree with the fact that the virtual failure of the Non-Cooperation Movement and the gloom that descended on the nationalist scene, created conditions for revolutionary activities ? Discuss.,,
(c). Planning was seen as a powerful instrument that could be used to remove regional inequality. Examine.
Q4. (a) “In the divided and contestable space of Indian politics, Gandhiji could claim for himself a centrist position because he alienated neither and tactically combined the goal of the moderates with the means of the extremists." Discuss.
(b) "After Indian Independence India-China relations started on a high note, but during the course of the coming years India had to face a bitter experience due to the Chinese aggression." Elaborate.
(c) “The Reorganisation of the States on the basis of language was a major aspect of national consolidation and integration.” Comment.
SECTION 'B'
Q5. Critically examine the following statements in about 150 words each:
(a) “The principles of Enlightenment were in some ways a continuation of the discoveries and theories of the Scientific Revolution."
(b) "The causes of the French Revolution of 1789 included both long term and structural factors, as well as more immediate events."
(c) "Industrial Revolution had far reaching social and political consequences with the advent of assembly line factories, urbanization and rise of the urban working class."
(d) "The multitude of newly independent countries came to be known as the “Third World', belonging neither to the First World of capitalist democracies, nor the Communist Second World."
(e) "The British were slated to withdraw from Palestine in May 1948, and both sides prepared for that day. Violence between Arabs and Jews, a already endemic, escalated."
Q6. (a). "Napoleon was not a revolutionary but he solidified many of the revolutionary changes of 1789 - 1791 and he himself supported most of the ideas and proposals of Enlightenment philosophers.".Substantiate.,
(b) "Lincoln's main thesis was that the Slavery issue had to be decided one way or the other and could no longer be evaded by compromise." Comment in the light of his role in the American Civil War.
(c) "The 1848 revolutions frightened the crowned heads of Europe and caused several to abdicate. Those who remained were cognizant of the threats posed by liberalism, nationalism and socialism.” Comment. 10
Q7 (a) "From Bismarck's 'Blood and Iron' speech and his forceful actions to achieve German unification, Bismarck came to be known as the Iron Chancellor.” Critically examine.
(b) Do you agree with the statement that the Second World War was history's most destructive war ? Elaborate.
(c) Discuss the circumstances leading to the French exit from Algeria in 1962.
Q8.(a) How did Stalin build on Lenin's legacy of Bolshevik Revolution and introduce new elements of totalitarianism to transform USSR as a superpower?
(b) A new configuration of power emerged in world politics after the end of the cold war. Analyse how USA managed to become the sole superpower. 20
(c) Critically examine whether it was true that after a century of dependency on Europeans, Africans were ill prepared for the task of nation-building.
UPSC Mains Exam 2019 - HISTORY
Time Allowed : 3.00
Hrs Maximum Marks : 250
(Paper-1) SECTION 'A'
Q1. Identify the following places
marked on the map supplied to you and write a short note of about 30 words on
each of them in your Question-cum-Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of
the places marked on the map are given below seriatim.
(i) Brick temple site
(ii) Early Harappan site
(iii) Ancient seaport and trade centre
(iv) Stone age site
(v) Neolithic site
(vi) Archaeological site
(vii) Ancient capital city
(viii) Ancient capital
(ix) Harappan site
(x) Ancient inscriptions site
(xi) A Rock-cut cave site
(xii) Ancient capital city
(xiii) Famous temple site
(xiv) Centre of School of art
(xv) Ancient inscriptional site
(xvi) Ancient education centre
(xvii) Pre-Harappan site
(xviii) Chalcolithic period site
(xix) Early inscriptional site
(xx) Ancient petroglyphs site
Q2. (a) Do you agree that archaeological evidence often
helps in the better understanding of literary sources ? Comment. 15
Marks
(b) The development of art and architecture during the Sunga period
belies the belief that they were anti-Buddhist. Discuss. 15 Marks
(c) Did the mastery over agriculture act as a leverage for the rise
of Harappan towns and cities ? Discuss. 15 Marks
Q3(a) The flourishing international trade during the
Kushana period gave tremendous impetus to the development of art.
Discuss. 15 Marks
(b) Examine how the transformation of the Varna system from the
Rigvedic to the Later-Vedic period affected the position women. 15
Marks
(c) There are no literary sources for the Harappan culture and non
archaeological evidence for the vedic period Explain the phenomenon . 20 Marks
Q4(a) Explain how Ashoka used religion as a tool of
political, aggrandizement ? 15 Marks
(b) Do you agree that the system of land grants from the
Gupta-Vakataka Period was connected with the decentralisation of state in any
way ? 20 Marks
(c) The discovery of monsoons by Hippalus gave a new direction to
Indo-Roman trade during the Satavahana period. Comment. 15 Marks
SECTION 'B'
Q5. Answer the following questions in about 150 words
each :
(a) Discuss how Vijayanagar empire became the cultural
capital of the south ? 10 Marks
(b) Examine the status of Sanskrit in Mughal India. 10 Marks
(c) Assess the rule of Zainul Abedin in Kashmir. 10 Marks
(d) The economic measures of Alauddin Khalji were aimed at greater
political control. Discuss. 10 Marks
(e) Examine the European impact on Mughal paintings. 10 Marks
Q6(a) Assess the statement that 'the philosophy of
Shankaracharya revolutionised religious thoughts in India’. 20 Marks
(b) Delineate the state of agriculture during the Sultanate
period. 15 Marks
(c) Sufi and Bhakti thoughts ennobled Indian psyche amidst
the vagaries of time. Elucidate. 15 Marks
Q7(a) The emergence of early capitalism in the
Mughal period was primarily due to urbanisation and commercialisation.
Comment. 20 Marks
(b) Internal strife and conflict beset with personal ambitions was
enough of an invitation for the Ghurids to invade India. Discuss. 15
Marks
(c) The Mughals built like Titans and embellished like jewellers.
Comment. 15 Marks
Q8(a) Critically analyse whether the success of the
Mughals is to be credited to their robust Jagirdari and Mansabdari
system. 15 Marks
(b) It was as much the court intrigues as also the defiance of the
provincial powers that hastened the decline of the Mughals in the 18th century.
Comment. 20 Marks
(c) Shivaji was not merely a military conqueror but also was an
enlightened ruler. Discuss. 15 Marks
UPSC Mains Exam 2019
- HISTORY (Paper-2)
Time Allowed : 3.00 Hrs
Maximum
Marks : 250
Section A
Q1. Critically examine
the following statements / Answer the following in about 150 words each:
10x5=50
(a) "Tipu Sultan was
trying to build in Mysore a strong centralized and militarized state, with
ambitious territorial designs." 10 Marks
(b) "Not until independence, when economic development became
a conscious and pursued policy, did the Railways begin to realize their
potential for assisting in the transformation of the Indian
economy." 10 Marks
(c) "Two important intellectual criteria which informed the
reform movements were rationalism and religious universalism." 10 Marks
(d) " ... the Kol Insurrection was mainly a war of the tribal
inhabitants of Chotanagpur against the non-tribal settlers and
service-holders." 10 Marks
(e) "The Cripps Mission was plagued throughout, and ultimately
torpedoed." 10 Marks
Q2.(a)How far was the drain theory a focal point of nationalist
critique of colonialism? 20 Marks
(b) Examine the forces at work for the introduction of western
education in India. Analyse the thrust given to it by the Christian
Missionaries. 20 Marks
(c) Do you subscribe to the view that the Anglo-French tussle in
Carnatic demonstrated the internal decay of the provincial chieftains of South
India.? 10 Marks
Q3(a) How would you explain the major trends of the
Swadeshi Movement in Bengal? 20 Marks
(b) Is it justified to say that the Government of India Act of 1935
had all brakes, but no engine ? 20 Marks
(c) How far was the widow remarriage movement effective in arousing
social concern for Indian women ? 10 Marks
Q4(a) Why is the Quit India Movement characterized as a
'Spontaneous Revolution’? Did it accelerate the process of Indian
independence? 20 Marks
(b) Assess the role of Subhas Chandra Bose in India's struggle for
independence. 20 Marks
(c) How did the introduction of Community Development Programme and
Panchayati Raj promote welfare of rural India? 10 Marks
SECTION B
Q5. Critically examine
the following statements in about 150 words each: 10x5=50
(a) "The arguments of
the free traders were a curious mixture of economic hard-headedness, social
benevolence, cosmopolitan idealism and class prejudice." 10 Marks
(b) "There are many ways in which the war of 1914 - 18 was
unprecedented, and in human history, entirely novel." 10 Marks
(c) "The ineffectiveness of the League of Nations to prevent
or to check Japanese aggression against China was the first serious blow to its
prestige as an agency for providing security." 10 Marks
(d) "Non-alignment came to symbolize the struggle of India and
other newly independent nations to retain and strengthen their independence
from colonialism and imperialism.” 10 Marks
(e) How would you explain the nature of pre-Marxian
Socialism? 10 Marks
Q6(a) How did the policies of
governments facilitate the process of industrialization in Europe? 20
Marks
(b) How was Italy transformed from 'a geographical expression' to
nation state? 20 marks
(c) How far did the Napoleonic preferential stance to help out the
French economy result in embroiling France in continental conflicts? 10
Marks
Q7(a) Which factors would you attribute to the British
colonial intervention in Malaya in the 19th century? How did Malays react to
British colonial rule? 20 marks
(b) Explain why Latin America was beset with chronic political
instability and endemic military conflicts throughout most of the 19th century. 20
Marks
(c) Do you agree with the view that the formation of NATO marked a
revolution in American attitude to the world problems? 10 Marks
Q8. (a) Do you subscribe to
the view that Greek War of Independence was mired in contrasts of the best and
the worst episodes? How did affect the Concert of Europe? 20 Marks
(b) Was Czechoslovakia served on a dish to Hitler at Munich? What
were its implications? 20 Marks
(c) Analyse the role of Egypt after the Second World War in
bringing about Arab unity. 10 Marks
UPSC Mains Exam 2018 -
HISTORY
Time Allowed : 3.00 Hrs
Maximum Marks : 250
(Paper-1) SECTION – "A"
1. Identify the following
places marked on the map supplied to you and write a short note of about 30
words on each of them in your Question cum Answer Booklet. Locational hints for
each of the places marked on the map are given below seriatim. (2.5 x 20 = 50
Marks)
1. Megalithic burial
site
2. Early
Agricultural centre
3. Chalcolithic
site
4. Early
Harappan site
5. Cave
Paintings
6. An
ancient temple
7.
Paleolithic site
8. Political
and Cultural centre
9. Political
and Cultural centre
10.
An ancient sea port
11. Terracotta
centre
12.
Buddhist centre
13.
Harappan site
14.
Inscriptional site
15.
Vaishnava cultural site
16.
An ancient capital
17.
Painted Grey Ware site
18.
A Jaina centre
19.
Chalcolithic site
20.
An ancient capital
2.(a) How did the early
Indian historical tradition, as reflected in Itihasa Purana, emerge? What are
the distinctive features of this genre? (20 Marks)
2.(b) “Archaeological
evidence does not give direct access to the possible social and political
dimensions of the decline of the Harappan civilization. What it does indicate
very clearly is that the Harappan culture underwent a gradual process of
de-urbanisation”? Comment. (15 Marks)
2.(c) Give
an account of gana-sanghas (non-monarchical state systems)? Why did they
decline? (15 Marks)
3.(a) Do
you agree with the popular view that Mauryas established a unitary and highly
centralized if not monolithic state system?(20 Marks)
3.(b) The
concept of Shramanic religions, with particular reference to Buddhism, had
their roots in Upanisadic ideas. Discuss. (15 Marks)
3.(c) “Doubtless
it was not a free state it was any rate a state” (K.A.N.Sastri), Reflect upon
the nature of local self government institutions in the Chola country.” (15
Marks)
4.(a) What
was the impact of trans-regional and trans-continental trade in the post
Mauryan period on social and cultural life of India? (20 Marks)
4.(b) “Utpanna
dravide bhakthi, Karnate vriddhimagata I Sthita kinchit maharashtre gurjare
jirnatam gata II - Padmapurana Account for the emergence of bhakti in Dravida
desa. (15 Marks)
4.(c) Discuss
the experimentations with art and architecture during the Gupta-Vakataka
period. (15 Marks)
SECTION
– "B"
5. Answer the following
questions in about 150 words each:
5(a) “The battles of
Tarian and Chandawar laid the foundations of Turkish rule in India”. Elaborate.
(10 Marks)
5(b) Discuss
evidence on slavery provided by Ibn Batuta with special reference to female
slaves. (10 Marks)
5(c) Discuss
the advancement made in Textile Technology under the Delhi Sultans.(10 Marks)
5(d) “Akbar
wished to assert his strong belief in God, but his concept of the way god is to
be worshipped was independent of either ourthodox Islam or Hinduism.” Comment.
(15 Marks)
5(e) Discuss
the literature written in Hindi in Mughal India. (10 Marks)
6(a) Critically
analyze the changing nature of caste and gender relations during the early
medieval period. (15 Marks)
6(b) “An
important feature of agriculture in Mughal India has been the large number of
crops raised by the peasants.” Illustrate by giving examples.(15 Marks)
6(c) “The
policy of creating heterogeneous nobility by Muhammad Tughlaq started the
process of disintegration of Delhi Sultanate.” Explain.
7(a) Do
you agree that convergence of political vacuum and impact of Islamicate culture
and polity
7(b) Describe
the new architectural features added by successive Sultans in the construction
of Tombs in India. (20 Marks)
7(c) What
was the role of Sufi Folk literature in the diffusion of Islam in India in
general and in Deccan in particular. (15 Marks)
8(a) Discuss
the working of Zamindari System under the Mughal rulers. Also describe the role
played by the Zamindars in the agrarian economy of Mughal India. (20 Marks)
8(b) “The
art of building was carried to highest degree of perfection under Shahjahan”.
Illustrate by giving architectural details of two of his most celebrated
buildings. (15 Marks)
8(c) “The
Afghan invasions in the Eighteenth Century not only signified the military
irrelevance of the Mughal Empire but also hastened its decline.” Explain.(15
Marks)
UPSC Mains Exam 2018 -
HISTORY (Paper-2)
Time Allowed : 3.00 Hrs
Maximum Marks : 250
SECTION
– "A"
Q1. Critically examine the
following statements in about 150 words each: (10×5=50)
(a) “The Battle of
Plassey (1757) thus marked beginning of political supremacy of the English East
India Company in India.” (10 Marks)
(b) “The
passing of the land from the hands of the peasant proprietors into the hands of
non-cultivating landlords brought about increasing polarization of classes in
agrarian areas.” (10 Marks)
(c) “Faced
with the challenge of the intrusion of colonial culture and ideology an attempt
to reinvigorate traditional institutions and to realize the potential of
traditional culture developed during the nineteenth century.” (10 Marks)
(d) “An
ideology of paternalistic benevolence, occasionally combined with talk of
trusteeship and training towards self-government, thinly veiled the realities
of a Raj uncompromisingly white and despotic.” (10 Marks)
(e) “States‟
reorganization did not, of course, resolve all the problems relating to
linguistic conflicts.” (10 Marks)
Q2.(a) Was the Moplah
Rebellion in Malabar an expression of anti-landlord and anti-foreign
discontent? Discuss. (20 Marks)
(b) Analyse
various trends in Dalit Movements in various parts of postindependent India.
(20 Marks)
(c) Could
Dyarchy 1919 satisfy the national sentiments of the Indians? (10 Marks)
Q3.(a) Underline the
growth of various forms of Socialist ideologies in the Indian National Movement
between World Wars I and II. (20 Marks)
(b) Trace
the development of land reforms in India between 1947 and early 1960‟s. (20
Marks)
(c) What
was the significance of Orientalist-Anglicist controversy in nineteenth century
India? Analyse. (10 Marks)
Q4.(a) Do you consider the
suspension of Non-Cooperation Movement a “national calamity.”? (20
Marks)
(b) Critically
examine the turns and twists in the politics of partition in 1930‟s and 1940‟s.
(20 Marks)
(c) Can
methods and policies of the moderates be referred to as „political
mendicancy‟? (20 Marks)
SECTION
– "B"
Q5. Critically examine
the following statements in about 150 words each: (10×5=50 Marks)
(a) “With the writings
of Karl Marx, Socialism assumed the form of Scientific Socialism.”
(b) “The
American War of Independence transformed Europe as well as America.”
(c) “The
American War of Independence transformed Europe as well as America.
(d) At
the end of the Battle of Sedan (1870), “Europe lost a mistress and gained a
master”.
(e) “Until
December 1941, the battlefield of the Second World War was exclusively European
and Atlantic; thereafter it became also Asiatic and Pacific.”
Q6.(a) Explain the major
ideas of Enlightenment. Discuss the contribution of Rousseau in Enlightenment.
(20 Marks)
(b) Discuss
how Japan Industrialized after the Meiji Restoration, What were the
consequences for its neighbours? (20 Marks)
(c) Explain
the features of Apartheid in South Africa. (15 Marks)
Q7.(a) Examine the role of
Bismarck in state building in Germany.
(b) Discuss
the factors constraining development of Africa after decolonization
(c) Outline
the circumstances leading to adoption of Marshall Plan.
Q8.(a) In the Chinese
Revolution of 1949, the elements of communism and nationalism were discernible.
Explain the statement in the light Mao‟s strategy which was different from that
of Lenin.
(b) Discuss
how far the United Nations has been successful in resolve global disputes from
year 1946 to 1991.
(c) Review
the policy of Glasnost adopted by Gorbachev.
UPSC
Mains Exam 2017 HISTORY
(Paper-1)
Marks: 250 Time Allowed: 3
Hours
SECTION – A
Q1. Identify the following places marked on the map supplies to
you and write a short note of about 30 words on each of them in your
Question-cum-Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of the places marked on
the map are given below seriatim. (2.5x20=50
Marks)
(i) A Prehistoric
cave-paintings' site
(ii) A Neolithic-Chalcolithic
site
(iii) An
Early Harappan site
(iv) A
Harappan site
(v) An
ancient capital city
(vi) A
Painted grey ware site
(vii) A
Neolithic site
(viii) A site
of Ashokan inscriptions
(ix) An
ancient port and trade centre
(x) A
Harappan site
(xi) A Chalcolithic
site
(xii) An
ancient capital city
(xiii) A
Rock-cut cave site
(xiv) A early
fortified city
(xv) A
Rock-cut temple site
(xvi) An
ancient temple site
(xvii) An
ancient capital city
(xviii) An
ancient temple site
(xix) A
Palaeolithic site
(xx) An ancient
capital city
Q2.
(a) Art and culture
are reflected to a far greater extent than political history in the epigraphic
sources. Comment. (15 Marks)
(b) The
second urbanization gave rise to the organized corporate activities that
reached their zenith during the Gupta period. Discuss. (20 Marks)
(c) The
emergence of Non-Harappan Chalcolithic cultures in Central India and the Deccan
mark a change not only in the subsistence pattern of people but an overall
transition from pre to proto historic period. Critically analyze. (15 Marks)
Q3.
(a) Critically
examine various views regarding the Vedic-Harappan relationship in light of the
latest discoveries. (15 Marks)
(b) "The
concept of Ashoka's Dhamma as found through his inscriptions had its roots in
Vedic-Upanishadic literature." Discuss. (15 Marks)
(c) The
period of Indian History form 3rd century B.C.E. to 5th century
C.E. was the period of innovation and interaction. How will you react ? (20 Marks)
SECTION – B
Q5. Answer the
following question in about 150 words each: (10x5=50 Marks)
(a) The 11th -
12th centuries C.E. saw eventful progression in the cultural
history of India. Discuss.
(b) Evaluate the accounts of
foreign travellers about the Vijayanagar Empire.
(c) Critically examine the 'blood
and iron' policy of Balban.
(d) Do you consider the
Rajatarangini of Kalhana to be a reliable source of the political history of
Kashmir ? Why?
(e) The religion of the Sikhs was
the main force of their unity. Comment.
Q6.
(a) To what extent
was the Caliphate the source and sanction to the legal authority of the Sultans
of Delhi ? (15 Marks)
(b)
"Bhakti and Sufi movements served the same social purpose."
Discuss. (15 Marks)
(c) Delineate
non-agricultural production and urban economy in the 13th and
14th centuries C.E. (20 Marks)
Q7.
(a) Do you agree that
the schemes of Muhammad bin Tughluq were correctly conceived badly executed and
disastrously abandoned ? Discuss.
(b) Do you think that Akbar's
Rajput policy was a conscious attempt to incorporate the Indian ruling elite
with the Mughal Imperial System ?
(c) "The political
disintegration was responsible for the socio-economic decline in India during
the 18th century." Comment.
UPSC
Mains Exam 2017 HISTORY
(Paper-2)
Marks: 250
Time Allowed: 3
Hours
SECTION – A
Q1. Critically examine the following statements in about 150
words each : (10x5=50 Marks)
(a) "The
Maratha polity disintegrated through internal stress."
(b) "The chief value of
Raja's (Raja Rammohan Roy) labours seems to lie in his fight against the forces
of medievalism in India."
(c) "The British railway
construction policy in India benefitted British economy in the nineteenth
century."
(d) The Arya Samaj may quite
logically be pronounced as the outcome of condition imported into India from
the West."
(e) "Sri Narayana Guru's was
a major intervention in the social reform movement from a subaltern
perspective."
Q2.
(a) Explain the
factors responsible for the recurrence of famines in the nineteenth century.
What remedial measures were adopted by the British Indian Government ? (20 Marks)
(b) Assess the role of press in
arousing awareness on important social issues in the second half of the
nineteenth century. (20 Marks)
(c) Underline the major
considerations of the British imperial power that led to the annexation of
Punjab. (10 Marks)
Q3.
(a) Trace the
origin of the Ghadar movement and discuss its impact on the revolutionaries in
India. (20 Marks)
(b) Explain why the efforts at
finding solution to India's constitutional impasse failed during
1942-1946. (20 Marks)
(c) Discuss the nature of peasant
movements under the Kisan Sabhas during 1920-1940. (10 Marks)
Q4.
(a) Discuss how the
Satyagrahas of Gandhi removed the spell of fear among Indians and thus knocked
off an important pillar of imperialism. (20 Marks)
(b) How far the developments in
science and technology in post-Independence period put India on the path of
modernity ? (20 Marks)
(c) Throw light on the nature of
'Instrument of Accession' and 'Standstill Agreement' signed by the Princely
State with the Indian Union. (10 Marks)
SECTION – B
Q5. Critically examine the following statements in about 150 words
each : (10x5=50 Marks)
(a)
"Kant's redefinition of reason and his rehabilitation of conscience marked
a high point in the intellectual reaction against dominant rationalism of the
Enlightenment."
(b) "The spirit behind the
great reforms of Napoleon's Consulate at home was the transference of the
methods of Bonaparte the general to task of Bonaparte the statesman."
(c) "The roots of the
Chartist movement in Great Britain were partly political and partly
economic."
(d) "18 January, 1871 had
been a day of triumph for the strength and pride of Germany and 28 June, 1919
was the day of chastisement."
(e) "The collapse of Berlin
Wall on 9 November, 1989 brought new meaning to the idea of cooperation in
Europe."
Q6.
(a) Explain why
England became the harbinger of Industrial Revolution. Also throw light on its
social consequences. (20
Marks)
(b) Why was the
First World War termed as the first 'total' war in modern history ? (20 Marks)
(c) Discuss how
agrarian crisis accompanied by severe industrial depression triggered the
Revolutions of 1848. (10
Marks)
Q7.
(a) What determinant
factors, along with diplomatic, shaped the process of German Unification ? (20 Marks)
(b) Examine the
statement that "the danger of 'Bolshevism' dominated not only the history
of the years immediately following the Russian Revolution of 1917 but the
entire history of the world since that date." (20 Marks)
(c) Examine why
Bolivar's failed to fructify in bringing about united stand of the Latin
Americans. (10
Marks)
Q8.
(a) Examine the
circumstances which led to the overthrow of democracy and the establishment of
Fascist dictatorship in Italy. (20 Marks)
(b) "By
1980s, the Communist System of Soviet Union was incapable of maintaining the
country's role as a Superpower." Substantiate. (20 Marks)
(c) Examine the
nature of Dutch imperialism in Indonesia. (10 Marks)
UPSC Mains Optional History Exam Paper - 2016
(Paper -1)
Section-A
1. Identify the following places marked on the map
supplied to you and write a short note of about 30 words on each of them in
your Question-cum-Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of the places
marked on the map are given below seriatim: 2.5x20=50 marks
(i) A Mesolithic
site
(ii) A Neolithic site
(iii) A Megalithic Chalcolithic site
(iv) A Neolithic site
(v) A Neolithic site
(vi) A Megalithic site
(vii)A site known for Buddhist remains
(viii) A Harappan site
(ix) A Harappan site
(x) A Harappan site
(xi) A Neolithic site
(xii)A Harappan site
(xiv) A capital city
(xiv) A rock-cut cave site
(xv) A late Harappan site
(xvi) An educational centre
(xvii) A terra-cotta art centre
(xviii) A seaport
(xix) A capital city
(xx) A capital city.
2.(a) Delineate and account for the regional characteristics of the Neolithic period in India. 15 marks
(b) Explain why the majority of the known Harappan settlements are located in the
semi-arid areas with saline groundwater. 20 marks
(c) In what way was the egalitarian character of the carly Vedic society
changed during the later Vedio poriod? 15 marks
3.(a) Examine the
relationship among economic growth, urbanization and State formation from c.
7th century BCE to 3rd century BCE. 15 marks
(b) How does the numismatic evidence of the period reflect the political and
economic outlook of the Kushanas and the Satavahanas? 15 marks
(c) The changes in the field of art from the Kushana period to early medieval
period arc incre reflection of changing outlook." Comment. 20 marks
4.(a) Critically
evaluate the theory and practice of land revenue system in ancient India. 20
marks
(b) The copious references to the preservation of Varnashrama system by the
kings eulogized in inscriptions are mere reflection of the Smriti
tradition." Discuss. 15 marks
(c) How did the temples of South India, as financial institutions, have deep
impact on the social institutions of carly mcdicval period? Critically examine.
15 marks
SECTION=B
5.(a) Evaluate the contents of the Tabaqat-i-Nasiri as a
source of medieval history. 10 marks
(b) Analyze the significance of the Uttaramerur inscriptions of the Chola King
Parantaka I. 10 marks
(c) Evaluate Jonaraja's account of the reign of Zain-ul-Abidin. 10 marks
(d) Comment on the veracity of Alberuni's account of the Indian society. 10
marks
(e) Delineate the development of the Mughal painting during the reign of
Jahangir. 10 marks
6.(a) Explain the
ingredients of the transitory nature of the early medieval India. 15 marks
(b) What measures were initiated by the Sultans for the consolidation of the
Delhi Sultanate? Discuss. 15 marks
(c) Identify the broad contours of the Mughal foreign policy and their impacts
on the Mughal empire. 20 marks
7.(a) "The
Advaita doctrine of Shankara cut at the very root of Bhaktivada." Do you
agree? 15 marks
(b) Do you think that the economic measures introduced by the Sultanate rulers
were beneficial to the common people as well? Illustrate with examples. 20
marks
(c) Assess the contribution of Firoz Shah Bahamani and Mahmud Gawan in the
field of education. 15 marks
8.(a) Do you think
that the agrarian crisis of the 17th century led to the disintegration of the
Mughal empire? Discuss. 20 marks
(b) Was it the weakening of the Mughal empire or the rise of regional powers
that led to the British conquest of India? Discuss. 15 marks
(c) Is it true that the court intrigues and weak revenue system led to the
collapse of the Maratha empire? Comment
UPSC IAS Mains Optional History (Paper -2) Exam Paper 2016
SECTION A
1. Answer the following in about 150
words each: 10x5=50 marks
(a) Comment on the
French ambition of building a territorial empire in India. 10 marks
(b) After the Battle of Plassey, how did India transit from the medieval to the
modern age? 10 marks
(c) Do you agree with the view that the growth of vernacular literature in the
19th and the 20th centuries paved the way for social reform and cultural
revival in India ? 10 marks
(d) "The Mutiny of 1857 was much more than a Mutiny of Sepoys and much
less than a National Rebellion." Comment. 10 marks
(e) Explain "Constructive Swadeshi" characterised by atmashakti
(self-reliance), which propelled the Swadeshi Movement in Bengal. | 10 marks
2.(a) How far is it correct to say that if Clive was the founder of the British
Empire in India, Warren Hastings was its administrative organiser ? 20 marks
(b) "Peace hath her victories no less renowned than war." Examine
this statement with reference to Lord William Bentinck. 20 marks
(c) "India's need for a federal system was more an imperative than a
political choice." Do you agree? 10 marks
3.(a) Critically
examine the causes responsible for the phenomenon called de-industrialisation'
in India during the nineteenth century. 20 marks
(b) How far is it correct to say that the 19th century tribal uprisings are a
part of subaltern nationalism? 20 marks
(c) How did Dr. B.R. Ambedkar try to seek a political solution to the problem
of caste in India ? 10 marks
4.(a) "The
need to impose greater parliamentary control over the Company's affairs
increased during the decades (1773 - 1853) after Plassey." Elucidate. 20
marks
(b) What significant role did women play in the Indian National Movement ? 20
marks
(c) Critically examine the nature and scope of environmental movements in
Independent India. 10 marks
SECTION B
5. Answer the following in about 150
words each : 10x5=50 marks
(a) "Karl Marx
applied his critical intelligence to Wealth of Nations ... Where Smith had seen
only the sunlight, Marx saw only the shadows thrown upon the human scene by the
unimpeded exercise of individual liberty ..." Elucidate. 10 marks
(b) What is Metternich system? Assess its impact on Europe. 10 marks
(c) “League of Nations is a League of Notions." Comment. 10 marks
(d) Explain the main features of the US Federal Constitution. 10 marks
(e) What factors contributed to the emergence of a unipolar world? 10 marks
6.(a) Critically
examine the statement that the French Revolution was not caused by the French
philosophers but by the conditions of national life and by the mistakes of the
government. 20 marks
(b) "A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this
government cannot endure permanently, half slave and half free." Explain
Abraham Lincoln's perspective. 20 marks
(c) Trace the significant role played by Ho Chi Minh in Vietnam's struggle for
freedom. 10 marks
7.(a) How did Lenin
achieve an abrupt transition from a Monarchical autocratic to a Socialist
State? 20 marks
(b) Do you agree with the view that the Treaty of Versailles was a bad
compromise between a treaty based upon force and a treaty based on ideas? 20
marks
(c) Trace the growth of British imperialism in South Africa from 1800 to 1907.
10 marks
8.(a) Trace the
growth of Arab nationalism after the First World War. How far was it a reaction
to Oil imperialism ? 20 marks
(b) In what way did the political changes in Soviet Union influence the events
in Eastern Europe during the closing decades of the 20th century ? 20 marks
(c) Outline the circumstances leading to Détente. 10 marks
UPSC Mains 2015: History
Paper- I
1. Identify the following places marked on the map
supplied to you (on page 4 and write a short note of about 30 words on each of
them in your Quest ion-cum- Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of the
places marked on the map are given below : 2.5×20=50
i. A Neolithic site
ii. A Neolithic site
iii. A Harappan site
iv. A Megalithic site
v. A Harappan site
vi. A painted-Grey-ware site
vii. An inscriptional site
viii. An important ancient city
ix. An ancient port
x. A site of ancient cave-paintings
xi. A Buddhist site
xii. An educational centre
xiii. Brahroadeya village
xiv. An ancient capital
xv. An ancient capital
xvi. A temple site
xvii. An ancient capital
xviii. An ancient sea-port
xix. An archaeological temple site
xx. Harappan site
2. a. How far can the ancient Indian Shruti literature be used
as historical sources.
b. The decline of Harappan civilization was caused by ecological degradation
rather than external invasion. Discuss
c. “Archaeology known of no Aryans.only literature knows of Aryans “Examine
critically.
3. a. How far it correct to say that changes in the post
Vedic economy gave birth to new religious movement* in India?
b. Delineate the nature and impact of India’s contact with Wentern Ama and the
Mediterranean world during the Maury an period
c. “Not only does ancient Tamil literature furnish an accurate picture of
widely disparate classes, it also describes the social condition of Tamil
country as it was” Discuss
4. a. Trace the role of guilds and trade organisations in the
development of early Indian economy.
b. Kailasa temple built at Ellora marks the cultivation of rock-cut
architecture in India. Elucidate.
c. How could the local self-government under the Cholas adjust with their
centralised administrative structure?
5. Answer the following questions about 150 words each:
10×5=50
a. Give a brief account of the early medieval temple architecture of Katnmir.
b. Why is Mamallapuram famous?
c. Mention the salient feature. of the polity of Vijaynagar Empire under
Krishnadevaraya.
d. What measures did Baiban adopt to combat the Mongol menace?
e. How does Tuzuk-i-Babn testify that Babar had been a cultured man?
6. a. Do the evidence* of land ownership at our disposal
support the theory of the prevalence of feudalism in early medieval India?
b. Discuss in brief the land-revenue –system and judicial administration of The
Delhi Sultanate.
c. “Sufis and medieval mystic saints failed to modify either the religious
ideas and practices or the outward structure of Islamic/Hindu societies to any
appreciable extent.
7. a. Make an estimate of Rana Kumbha as a patron of literature
and art.
b. Why should the sixteenth century be regarded as the period of the Indian
Renaissance?
c. “Tantrism, if not in practice, at least on conceptual level challenged
patriarchy;’ Examine Tantrism specially keeping in mind the above context.
8. a. “In medieval Indian history Akbar was unique for his
religio-political ideas and policies.” Analyse this statement.
b. Will it not be correct to say that the rural economy in Mughal India was
relatively? self-sufficient?
c. Compare the Peshwas’ bureaucratic management with that of the Imperial
Mughal administration.
Paper–II
1. Critically examine the following statements in about
150 words each. 10 x 5=50
a. ‘Annexation of Punjab was part of a broad nort motion after the exit of
Maharaja Ranjit Singh.”
b. The Regulating Act (1773), the Pitt’s India Act (1784) and eventually the
Charter Act of 1833 left the East India Company as a mere shadow of its earlier
political and economic power in India.”
c. “The Indigo Revolt of 1859-60 holds a very significant place in our history
of national liberation movement. For the first time in the history of our
anticolonial struggle, its two independent currents— spontaneous peasants and
constitutional agitation in defence of the peasantry—came into mutual contact.”
d. “The very idea of the bomb and the secret society and of propaganda through
action and sacrifice were imports from the west”
e. “This retention of Roweltt legislation in the teeth of universal opposition
repeal is an affront to the nation. Its repeal is necessary to appraise
national honour.”
2. a. Swami Dayanand’s philosophy represents both elements of
extremism and social radicalism” Substantiate.
b. To characterize the quit India Movement as ‘ Spontaneous revolution’ would
be partial interpretation, so also would be to look up at it as the culmination
of Gandhian Satyagraha movements” Elucidate.
c. A powerful left-wing group developed in India in the late 1920s and 19 30s,
contributing to the radicalization of national movement.” Critically examine.
3. a. “Under the forceful thrust of British colonialism,
Indian economy was transformed into a colonial one, the structure of which was
determined by the requirements of Britain’s fast developing industrial economy
“ Examine.
b. “James Mill, the apostle of utilitarian philosophy, proposed a revolution
ofIndian society through the Sveapon of law’ solely. But in actual policy
framing, other influences and considerations weighed much more than the
colonial State.” Elucidate.
c. The Royal Indian Navy Revolt was seen as an event which marked the end of
the British rule almost as finally as Independence Day.” Explain
4. a. Analyze the nature of peasant movements during the
nationalist phase and bring out their shortcomings.
b. “Jawaharlal Nehru, though a declared socialist, was nr-ion focus on
providing building blocks to the making of a new India” Examine.
c. ‘Although the Government of India Act 1935 replaced diarchy with Provincial
Autonomy, the overriding powers of the Governor diluted the spirit autonomy.”
Elucidate.
5. Critically examine the following statements in about
150 words: 10×5=50
a. “France was even more fertile than Britain in producing new socialist
theories and movements, though bore less concrete results in France than
Britain.
b. “The multiple contradictions that quickly undermined the new edifice, had
been expressed even before the meeting of the Estates General in France. The
internal conflict among Estates had manifested itself.”
c. “The whole episode that is known as the July Revolution (1830) was fought
and won not for the establishment of an extreme democracy but to get rid of the
aristocratic and clericalist attitude of the restored Bourbons.”
d. “Mazzini’s conception of Italian nationality was not exclusive and his
dominant ideal was the recreation of moral unity of mankind.”
e. “The Constitutional blockade was a misconceived idea of economically
defeating Great Britain.”
6. a. “The Berlin congress (1878) failed to unlock the
Eastern Question Though there was no major war in Europe for nearly three
decades after the Treaty contained the seeds of many future wars” Critically
evaluate.
b. History of Africa appears to be simply an extension or mere sub-theme under
historiography, Africa and American history. According to this scramble
Elucidate without any history before the European scramble” Elucidate.
c. “The Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan were considered by the Russian
Bloc as a weapon against Russia in order to restrict her influence” critically
examine
7. a. How far is it correct to say that the First World War
was fought essentially for the preservation of the balance of power?
b. “The failure of Kuomintang against the communist onslaught was unimaginable
and it was Mao Tse-tung whose tenacity and innovative approach had accomplished
the unthinkable.” Discuss.
c. “The oppressive exploitation of the working class in the wake of Industrial
Revolution had jolted the social conscience of England.” Elucidate.
8. a. The UNO was created in the light of experience of the
‘League of Nations’ but out spite of the mandate contained in the UNO
constitution, its effective role maintaining world peace has lacked
cohesiveness and collective approach.” Examine.
b. “The European Union, a diplomatic marvel, continues to grapple with
intermittent fissures Arising qui oi economic contentious issues that pose a
challenge to an effective integration of the Union.” Critically examine
c. “The role of the Non-Alignment Movement in world affairs has suffered
greatly due to the theatre of internecine conflicts among the Third World
countries who spearheaded it” Elucidate.




An insightful read on tackling History for the UPSC Mains! The article provides a concise yet comprehensive approach, making it easier to grasp key events and themes. A must-read for aspirants aiming to ace the exam."
ReplyDeleteDigital Marketing Course In Hyderabad